money
money

money [money moneys monies] BrE [ˈmʌni] NAmE [ˈmʌni] noun 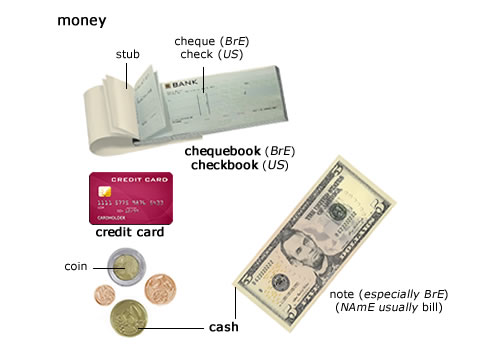
1. uncountable what you earn by working or selling things, and use to buy things
•to borrow/save/spend/earn money
• How much money is there in my account?
• The money is much better in my new job.
•If the item is not satisfactory, you will get your money back.
•We'll need to raise more money (= collect or borrow it) next year.
•Can you lend me some money until tomorrow?
•Be careful with that — it cost a lot of money.
2. uncountable coins or paper notes
• I counted the money carefully.
• Where can I change my money into dollars?
see also ↑funny money, ↑paper money, ↑ready money
3. uncountable a person's wealth including their property
• He lost all his money.
• The family made their money in the 18th century.
4. moneysor moniesplural (law or old use)sums of money
•a statement of all monies paid into your account You will find other compounds ending in money at their place in the alphabet.
more at the best that money can buy at ↑best n., careful with money at ↑careful, coining money at ↑coin v., see the colour of sb's money at ↑colour n., easy money at ↑easy adj., a fool and his money are soon parted at ↑fool n., it/money doesn't grow on trees at ↑grow, a licence to print money at ↑licence n., not for love or/nor money at ↑love n., marry money at ↑marry, expense, money, etc. is no object at ↑object, pay good money for sthyou pays your money and you takes your choice at ↑pay v., pots of money at ↑pot n., be rolling in money/it at ↑roll v., give sb a (good) run for their money at ↑run n., time is money at ↑time n.
Idioms: ↑for my money ▪ ↑get your money's worth ▪ ↑good money ▪ ↑have money to burn ▪ ↑in the money ▪ ↑made of money ▪ ↑make money ▪ ↑make money hand over fist ▪ ↑money for jam rope ▪ ↑money is no object ▪ ↑money talks ▪ ↑on the money ▪ ↑put money into something ▪ ↑put your money on somebody ▪ ↑put your money where your mouth is ▪ ↑throw good money after bad ▪ ↑throw money at something ▪ ↑throw your money about
Word Origin:
Middle English: from Old French moneie, from Latin moneta ‘mint, money’, originally a title of the goddess Juno, in whose temple in Rome money was minted.
Culture:
money
The US dollar is made up of 100 cents. The ↑Department of the Treasury prints bills (= paper money) in various denominations (= values): $1, $2, $5, $10, $20, $50 and $100. US bills are all the same size, whatever their value, and measure about 2×6 inches/6.5×15.5 centimetres. All are green and are sometimes called greenbacks. On the front, each has a picture of a famous American. The dollar bill, for instance, shows George ↑Washington, the first US president. An informal name for dollars is bucks, because in the early period of US history people traded the skins of bucks (= deer) and prices would sometimes be given as a number of buckskins. Buck refers to the dollar itself, and not to the bill. So although you can say ‘He earns 500 bucks a week’, you have to say ‘If I give you four quarters could you give me a dollar bill?’
The Treasury also makes US coins: pennies which are worth.01 of a dollar, nickels (.05), dimes (.10) and quarters (.25). There are also half dollars (.50) and silver dollars but these are not often seen. Pennies have a dark brown colour; all the other coins have a silver appearance.
When you write an amount in figures the dollar sign ($) goes to the left of the amount and a decimal point (.) is placed between the dollars and the cents (= hundredths of a dollar). If the amount is less than one dollar, the cent sign (¢) is put after the numbers. So you write $5, $5.62 and 62¢.
Britain’s currency is the pound sterling, written as £ before a figure. A pound consists of 100 pence, written as p with figures. Pound coins are round and gold-coloured. They have the Queen’s head on one side and one of four designs, English, Scottish, Welsh or Northern Irish, on the other. The £2 coin is silver-coloured with a gold edge. Coins of lower value are the silver-coloured 50p, 20p, 10p and 5p pieces, and the copper-coloured 2p and 1p pieces. All are round, except for the 50p and 20p pieces which have seven curved sides. Coins are made at the ↑Royal Mint. Paper notes (not bills), which have the Queen’s head on one side and a famous person, e.g. Charles Dickens, on the other, are worth £5, £10, £20 or £50.
A pound is informally called a quid, a £5 note is a fiver, a £10 note is a tenner. Scottish banknotes have their own designs. They can be used anywhere in Britain, though shops can legally refuse to accept them. To prevent people forging (= making their own) paper money, designs are complicated and difficult to copy. To check that a note is genuine, a shop assistant may hold it up to the light to see if it has a narrow silver thread running through it.
The decimal system now in use in Britain replaced the old pounds, shilling and pence, or LSD system in 1971. Formerly British money was in pounds, shillings and pence. There were 12 pence or pennies in a shilling, and 20 shillings in a pound. The old coins included the farthing (= a quarter of a penny) and the half-crown (= two shillings and sixpence). There were notes for 10 shillings, £1 and £5.
Gold guinea coins were used in the 18th century and were worth 21 shillings. Until 1971 prices were often set in guineas instead of pounds for luxury items, such as antiques and jewellery, for the fees of doctors, lawyers, etc, and at auctions, though the guinea coin had long since gone out of circulation. Some racehorses are still auctioned in guineas.
On 1 January 1999 the ↑euro system was introduced in 11 countries of the ↑European Union. Britain chose not to be part of this first group and no date was fixed for Britain to start using the euro. However, many British businesses have euro bank accounts so as to be able to pay for goods and be paid in euros and many shops in Britain accept payment in euros.
Thesaurus:
money noun
1. U
•The hospital is raising money for a new kidney machine.
funds • • finance • • capital • • means • |informal cash •
government/public money/funds/finance/capital/cash
have/lack the money/funds/finance/capital/means/cash (to do sth)
be short of money/funds/capital/cash
2. U
•I counted the money carefully.
cash • • change •
draw out/get out/take out/withdraw money/cash
ready money/cash (= money that you have available to spend immediately)
Money or cash? If it is important to contrast money in the form of coins and notes with money in other forms, use cash:
•Payments can be made by cheque or in cash.
✗ Payments can be made by cheque or in money.
3. U
•He lost all his money on the stock market in 2008.
wealth • • fortune • |often approving prosperity • |sometimes disapproving affluence • |literary riches •
have/possess/accumulate/acquire/inherit money/wealth/a fortune/riches
bring money/wealth/prosperity/affluence/riches
make money/a fortune (on/out of sth)
Collocations:
Finance
Income
earn money/cash/(informal) a fortune
make money/a fortune/(informal) a killing on the stock market
acquire/inherit/amass wealth/a fortune
build up funds/savings
get/receive/leave (sb) an inheritance/a legacy
live on a low wage/a fixed income/a pension
get/receive/draw/collect a pension
depend/be dependent on (BrE) benefits/(NAmE) welfare/social security
Expenditure
spend money/your savings/(informal) a fortune on…
invest/put your savings in…
throw away/waste/ (informal) shell out money on…
lose your money/inheritance/pension
use up/ (informal) wipe out all your savings
pay (in) cash
use/pay by a credit/debit card
pay by/make out a/write sb a/accept a (BrE) cheque/(US) check
change/exchange money/currency (BrE) traveller's cheques/(US) traveler's checks
give/pay/leave (sb) a deposit
Banks
have/hold/open/close/freeze a bank account/an account
credit/debit/pay sth into/take money out of your account
deposit money/funds in your account
withdraw money/cash/£30 from an ATM, etc.
(formal) make a deposit/withdrawal
find/go to/use (especially NAmE) an ATM/(BrE) a cash machine/dispenser
be in credit/in debit/in the black/in the red/overdrawn
Personal finance
manage/handle/plan/run/ (especially BrE) sort out your finances
plan/manage/work out/stick to a budget
offer/extend credit (to sb)
arrange/take out a loan/an overdraft
pay back/repay money/a loan/a debt
pay for sth in (especially BrE) instalments/(NAmE usually) installments
Financial difficulties
get into debt/financial difficulties
be short of/ (informal) be strapped for cash
run out of/owe money
face/get/ (informal) be landed with a bill for £…
can't afford the cost of…/payments/rent
fall behind with/ (especially NAmE) fall behind on the mortgage/repayments/rent
incur/run up/accumulate debts
tackle/reduce/settle your debts
Synonyms:
money
cash • change
These are all words for money in the form of coins or paper notes.
money • money in the form of coins or paper notes: ▪ I counted the money carefully. ◇ ▪ Where can I change my money into dollars? ◇ ▪ paper money ▪ ▪ (= money that is made of paper, not coins)
cash • money in the form of coins or paper notes: ▪ How much cash do you have on you? ◇ ▪ Payments can be made by cheque or ▪ in cash ▪.
money or cash?
If it is important to contrast money in the form of coins and notes and money in other forms, use cash: ▪ How much money/cash do you have on you? ◇ Payments can be made by cheque or in money. ◇ Customers are offered a discount if they pay money.
change • the money that you get back when you have paid for sth giving more money than the amount it costs; coins rather than paper money: ▪ The ticket machine doesn't give change. ◇ ▪ I don't have any ▪ small change ▪ ▪ (= coins of low value) ▪.
to draw out/get out/take out/withdraw money/cash
ready money/cash (= money that you have available to spend immediately)
Example Bank:
•All his money went on women.
•All their money was tied up in long-term investments.
•All these improvements will cost money.
•Did your parents give you pocket money when you were little?
•Government officials were siphoning off money for personal gain.
•Half the money raised was donated to charity.
•He contributed $180 000 in soft money= unregulated political donationsto the party committee.
•He felt sorry for her and took some money off her bill.
•He hoped the plan would bring in quite a bit of money.
•He made a fortune dealing on the money markets.
•He managed to persuade his friend to put up the money for the venture.
•He sank most of his money into his struggling business.
•He spent their rent money on beer.
•He squandered his money on gambling and drink.
•He started stealing as a way of making easy money.
•He stopped at the betting shop to put money on a horse.
•He thinks he can make friends by throwing his money around.
•He was charged with laundering money.
•He'll do anything for money!
•He's going to leave. I'd bet money on it.
•His prediction was right on the money.
•How much money did he earn last year?
•I don't have any money left.
•I don't know how much spending money to take on holiday.
•I don't know where all the money goes!
•I don't think they'll accept French money on the plane.
•I need to pay this money in today.
•I pay my money into the bank as soon as I get paid.
•I spent all the money on clothes.
•I'll have to get some more money from somewhere.
•I'll pay the money back next week, I promise.
•Investors were pouring money into Internet start-ups.
•Is this a good way to spend taxpayers' money?
•Money for the extension to the gallery came from the sale of old exhibits.
•Most of the money went to pay for food.
•Most of the money went to pay for the food and drink.
•She gave him $5 lunch money.
•She had two children to support and no money coming in.
•She lost a lot of money at the casino.
•She stashed the money away in the bank.
•Some of this money was funneled to secret CIA programs.
•Some people were in the street collecting money for charity.
•That painting is worth a lot of money.
•The Senate recognized the need to put more money in the pockets of dairy farmers.
•The boat trip lasts three hours, so you certainly get your money's worth.
•The bookmaker was quite happy to take his money.
•The collection box was full of coins and paper money.
•The company paid hush money to the victims to keep them quiet.
•The friends pooled their money to buy tickets.
•The hotel gives value for money.
•The manager was unwilling to refund my money.
•The money was transferred into an offshore bank account.
•The new airport terminal was built with oil money.
•The quality of public health care depends on the amount of money allocated to it.
•The smart money is on Brazil to win.
•The solution to inflation lies in the control of the money supply.
•The stallholders bank their money at the end of the day.
•The stores were very happy to take his money.
•There is big money in golf for the top players.
•These cars cost a lot of money.
•They demanded $1 million in ransom money.
•They owe lots of people money.
•They sensibly invested their prize money rather than spending it.
•They tend to throw money at problems without trying to work out the best solution.
•This money has been earmarked for public projects.
•We changed our money into dollars at the airport.
•We ran out of money and had to come home early.
•We're trying to set some money aside for a new car.
•Whenever I have a little extra money, I buy clothes.
•Where's the money for the milk?
•You could consider hiring a professional money manager.
•You might get some money off the price if it's an old model.
•an old miser who hoarded his money
•the best car that money can buy
•the large sums of money we handle in this store
•He hoped the project would make money.
•He lost all his money in the 1929 stock market crash.
•He returned the new TV to the store and got his money back.
•It has often been said that money is the root of all evil.
•The money is great in my new job.
|
|